Organic chemistry is a field that encompasses a vast array of compounds, each with its unique properties and applications. Among these compounds, tyramine stands out as an intermediate with significant implications in various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, food science, and neurochemistry. In this blog post, Viablife will share the effects of tyramine, an organic chemistry intermediate, and its role in different areas of research and industry.
What is Tyramine?
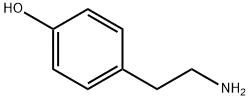
Tyramine is a naturally occurring trace amine and a phenethylamine derivative. It is structurally similar to the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine, which are crucial for brain function and mood regulation. Tyramine is found in a variety of foods, such as aged cheeses, cured meats, and fermented beverages. It is also synthesized in the body from the amino acid tyrosine.
Chemical Properties and Synthesis
Tyramine is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H11NO. It can be synthesized through various methods, including enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins and chemical synthesis from phenylalanine or tyrosine. The chemical properties of tyramine make it a versatile intermediate in the synthesis of other bioactive compounds.
Pharmacological Effects
1. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Tyramine has been studied for its potential as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor. MAOIs are drugs that inhibit the activity of monoamine oxidase enzymes, which break down neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin. By inhibiting these enzymes, tyramine can increase the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain, potentially leading to mood elevation and other therapeutic effects.
2. Interaction with Cheese and Medications: Tyramine in aged cheese can interact with certain medications, such as MAOIs and some antidepressants, leading to a hypertensive crisis. This is due to the inhibition of monoamine oxidase, which would normally break down tyramine, allowing it to accumulate and cause a sharp rise in blood pressure.
3. Potential Use in Weight Loss: Some studies suggest that tyramine may have appetite-suppressing effects, making it a potential candidate for weight loss therapies. However, more research is needed to fully understand its role and safety in this context.
Neurochemical Role
Tyramine is involved in the regulation of various physiological processes in the body, including:
1. Neurotransmission: As a precursor to neurotransmitters, tyramine plays a role in the transmission of nerve impulses across the synaptic cleft.
2. Stress Response: Tyramine has been implicated in the body's stress response, with increased levels observed during periods of stress.
3. Mood Regulation: Its structural similarity to dopamine and norepinephrine suggests that tyramine may influence mood and emotional states.
Food Science Applications
1. Flavor Development: Tyramine contributes to the development of flavors in aged and fermented foods, enhancing taste and aroma.
2. Food Safety: The interaction between tyramine and certain medications can pose a risk to individuals taking these drugs. Therefore, it is important for food manufacturers to be aware of tyramine content in their products, especially in foods that are likely to be consumed by individuals on specific medications.

Industrial Applications
1. Pharmaceuticals: As a precursor in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, tyramine is crucial in the development of new drugs.
2. Cosmetics: In the cosmetics industry, tyramine is used as a stabilizer and preservative in certain products.
3. Research and Development: Tyramine is a key intermediate in the synthesis of compounds used in scientific research, aiding in the discovery of new bioactive substances.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of tyramine and its production is relatively low compared to other chemicals. However, it is essential to ensure that any industrial processes involving tyramine are carried out with proper waste management and environmental controls in place.
Conclusion
Tyramine, an organic chemistry intermediate, has a wide range of effects and applications across multiple fields. From its role in neurotransmission and mood regulation to its use in food science and industrial processes, tyramine's impact is multifaceted.
Why Choose Viablife's Tyramine?
Viablife offers pure tyramine powder with a uniform particle size, synthesized via a biosynthetic process, ensuring higher purity with fewer impurities. Our meticulous control over particle size enhances fluidity. Inquire about our pharmaceutical intermediates for further collaboration!
By elucidating tyramine's potential in depression treatment, Viablife aims to contribute to mental health advancements with precision and efficacy.
Related products:
1. L-Tyrosine
2. Ceramide NP
Viablife
info@viablife.com

